New Delhi, Feb 02 : Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) in India continues to grow, driven by mandated laws and a corporate commitment to social and environmental causes. In FY 2022–23, over 24,000 companies collectively spent ₹29,986.92 crores across 40 states and union territories, funding 51,966 projects across 14 development sectors. These numbers not only highlight the financial contributions but also reflect the diverse priorities shaping India’s socio-economic fabric.
Key National Metrics
– Companies Participating: 24,392
– CSR Spend: ₹29,986.92 crores
– Projects Supported: 51,966
– Development Sectors: 14
– States Covered: All 40 states and UTs, with some key hotspots of activity.
Geographical Analysis
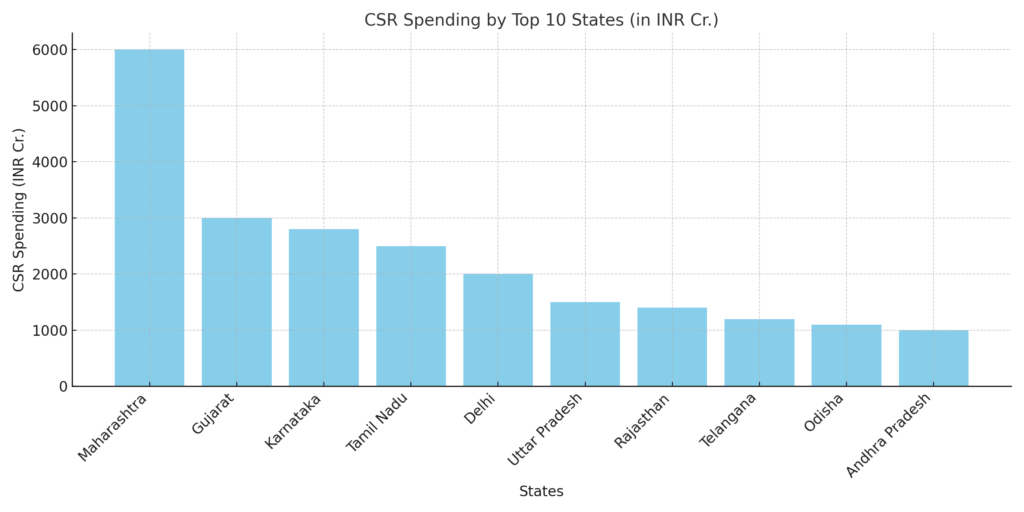
The geographical distribution of CSR spending showcases Maharashtra as the leading state, receiving the highest funds, followed by Gujarat, Karnataka, and Tamil Nadu. Maharashtra alone accounted for over ₹5,000 crores, likely attributed to its industrial hubs and corporate headquarters. States such as Odisha, Rajasthan, and Andhra Pradesh also saw significant contributions, particularly in rural areas where developmental needs are acute.
This data highlights an unequal distribution, as industrialized states attract more funding compared to remote or less developed regions.
Sectoral Allocation
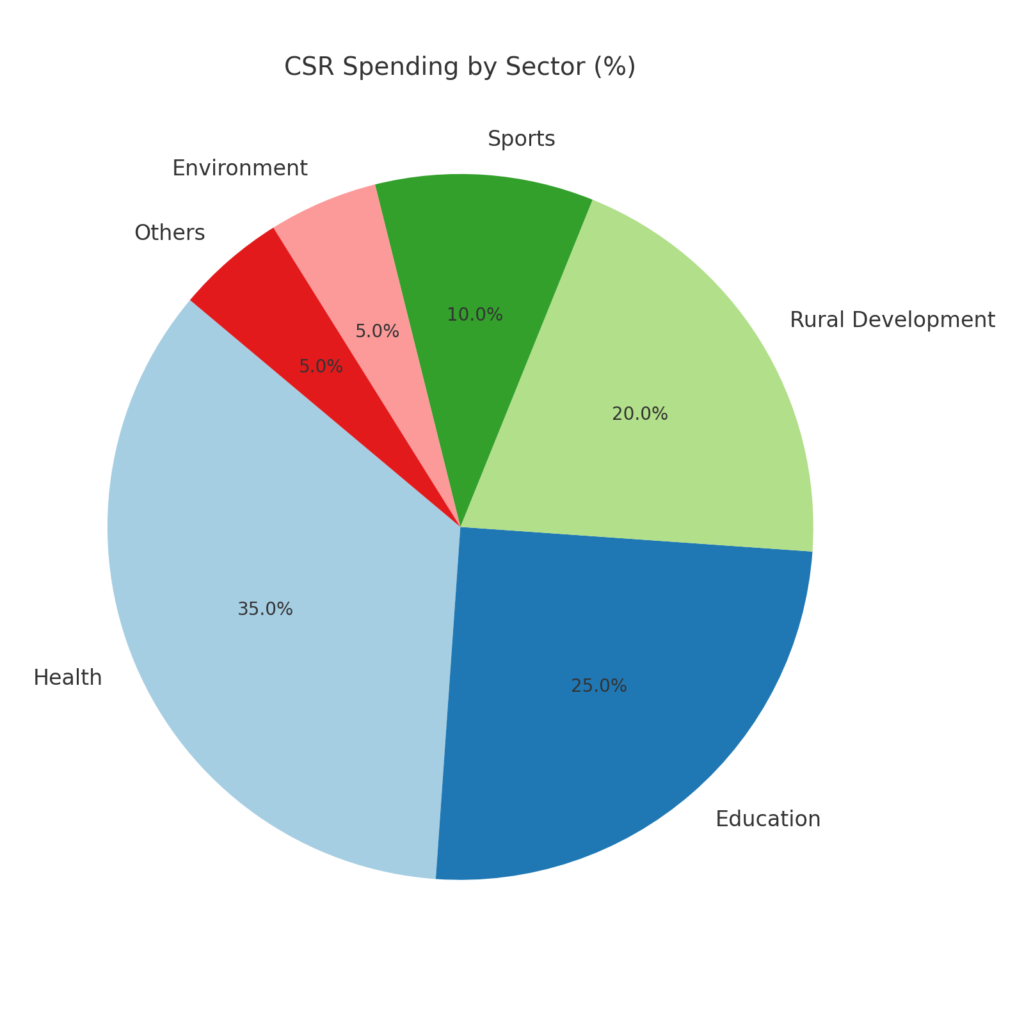
CSR contributions have prioritized development sectors that address India’s most pressing challenges:
1. Rural Development: Focused on sustainable rural upliftment through infrastructure, education, and livelihood programs.
2. Health and Sanitation: Includes healthcare infrastructure, hygiene campaigns, and pandemic response efforts.
3. Education, Development, and Livelihoods (EDL): Investments in skill-building, scholarships, and literacy programs to empower communities.
4. Swachh Bharat Initiatives: Supporting cleanliness and waste management under the national Swachh Bharat mission.
5. Encouraging Sports: Increasing participation in grassroots sports and infrastructure.
Notably, projects under the Clean Ganga Fund and environmental sustainability also received meaningful contributions, signaling growing attention to ecological issues.
Corporate Contributions: Top Players
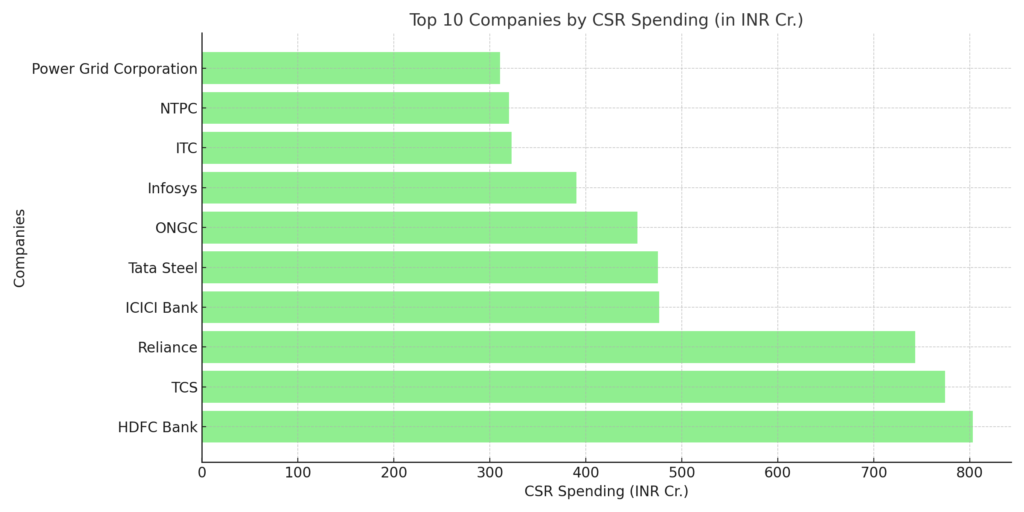
India’s largest corporations remain key drivers of CSR activities:
– HDFC Bank Limited leads with ₹803.15 crores, emphasizing financial inclusion and education.
– Tata Consultancy Services (TCS) and Reliance Industries followed closely, contributing ₹774.44 crores and ₹743.4 crores, respectively.
– Other prominent contributors include ICICI Bank, Tata Steel, ONGC, Infosys, and NTPC, spreading investments across multiple sectors.
PSU vs. Non-PSU Spending
Non-Public Sector Undertakings (Non-PSUs) contributed 86% (₹25,891.15 crores) of total CSR expenditure, while Public Sector Undertakings (PSUs) contributed the remaining ₹4,095.78 crores. This disparity underscores the dominant role of private corporations in driving CSR funding, although PSUs remain consistent contributors.
Compliance Patterns
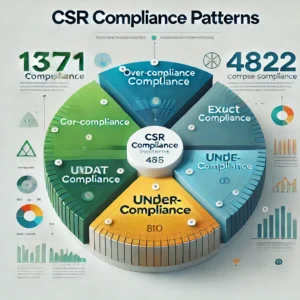
An analysis of CSR compliance reveals:
– Over-compliance: 13,571 companies exceeded their prescribed CSR budgets.
– Exact Compliance: 1,622 companies met the prescribed spending.
– Under-compliance: 4,855 companies fell short of their mandated CSR requirements.
– Non-compliance: Alarmingly, 810 companies reported zero CSR spending, highlighting areas for stricter regulatory enforcement.
Emerging Trends and Insights
– Focus on Long-Term Impact: Corporates are increasingly aligning CSR goals with national priorities such as rural development, healthcare, and sustainability.
– Regional Disparities: A need exists for equitable distribution to address underfunded regions like the North-East and rural hinterlands.
– Sector Diversification: While health and education dominate, other sectors like environmental sustainability, skill development, and disaster management are gaining traction.
Conclusion: Moving Forward
The CSR landscape in India paints a picture of commitment, innovation, and opportunity. With ₹30,000 crores invested in societal betterment, the impact is undeniable, yet challenges persist in ensuring fair distribution, increased compliance, and alignment with grassroots needs. By addressing these gaps, India’s CSR ecosystem can continue to evolve as a transformative force for inclusive development.